Caution
You're reading an old version of this documentation. If you want up-to-date information, please have a look at 0.9.1.
librosa.griffinlim_cqt¶
- librosa.griffinlim_cqt(C, n_iter=32, sr=22050, hop_length=512, fmin=None, bins_per_octave=12, tuning=0.0, filter_scale=1, norm=1, sparsity=0.01, window='hann', scale=True, pad_mode='reflect', res_type='kaiser_fast', dtype=None, length=None, momentum=0.99, init='random', random_state=None)[source]¶
Approximate constant-Q magnitude spectrogram inversion using the “fast” Griffin-Lim algorithm.
Given the magnitude of a constant-Q spectrogram (
C), the algorithm randomly initializes phase estimates, and then alternates forward- and inverse-CQT operations. 1This implementation is based on the (fast) Griffin-Lim method for Short-time Fourier Transforms, 2 but adapted for use with constant-Q spectrograms.
- 1
D. W. Griffin and J. S. Lim, “Signal estimation from modified short-time Fourier transform,” IEEE Trans. ASSP, vol.32, no.2, pp.236–243, Apr. 1984.
- 2
Perraudin, N., Balazs, P., & Søndergaard, P. L. “A fast Griffin-Lim algorithm,” IEEE Workshop on Applications of Signal Processing to Audio and Acoustics (pp. 1-4), Oct. 2013.
- Parameters
- Cnp.ndarray [shape=(n_bins, n_frames)]
The constant-Q magnitude spectrogram
- n_iterint > 0
The number of iterations to run
- srnumber > 0
Audio sampling rate
- hop_lengthint > 0
The hop length of the CQT
- fminnumber > 0
Minimum frequency for the CQT.
If not provided, it defaults to C1.
- bins_per_octaveint > 0
Number of bins per octave
- tuningfloat
Tuning deviation from A440, in fractions of a bin
- filter_scalefloat > 0
Filter scale factor. Small values (<1) use shorter windows for improved time resolution.
- norm{inf, -inf, 0, float > 0}
Type of norm to use for basis function normalization. See
librosa.util.normalize.- sparsityfloat in [0, 1)
Sparsify the CQT basis by discarding up to
sparsityfraction of the energy in each basis.Set
sparsity=0to disable sparsification.- windowstr, tuple, or function
Window specification for the basis filters. See
filters.get_windowfor details.- scalebool
If
True, scale the CQT response by square-root the length of each channel’s filter. This is analogous tonorm='ortho'in FFT.If
False, do not scale the CQT. This is analogous tonorm=Nonein FFT.- pad_modestring
Padding mode for centered frame analysis.
See also:
librosa.stftandnumpy.pad.- res_typestring
The resampling mode for recursive downsampling.
By default, CQT uses an adaptive mode selection to trade accuracy at high frequencies for efficiency at low frequencies.
Griffin-Lim uses the efficient (fast) resampling mode by default.
See
librosa.resamplefor a list of available options.- dtypenumeric type
Real numeric type for
y. Default is inferred to match the precision of the input CQT.- lengthint > 0, optional
If provided, the output
yis zero-padded or clipped to exactlylengthsamples.- momentumfloat > 0
The momentum parameter for fast Griffin-Lim. Setting this to 0 recovers the original Griffin-Lim method. Values near 1 can lead to faster convergence, but above 1 may not converge.
- initNone or ‘random’ [default]
If ‘random’ (the default), then phase values are initialized randomly according to
random_state. This is recommended when the inputCis a magnitude spectrogram with no initial phase estimates.If
None, then the phase is initialized fromC. This is useful when an initial guess for phase can be provided, or when you want to resume Griffin-Lim from a previous output.- random_stateNone, int, or np.random.RandomState
If int, random_state is the seed used by the random number generator for phase initialization.
If np.random.RandomState instance, the random number generator itself.
If
None, defaults to the current np.random object.
- Returns
- ynp.ndarray [shape=(n,)]
time-domain signal reconstructed from
C
See also
Examples
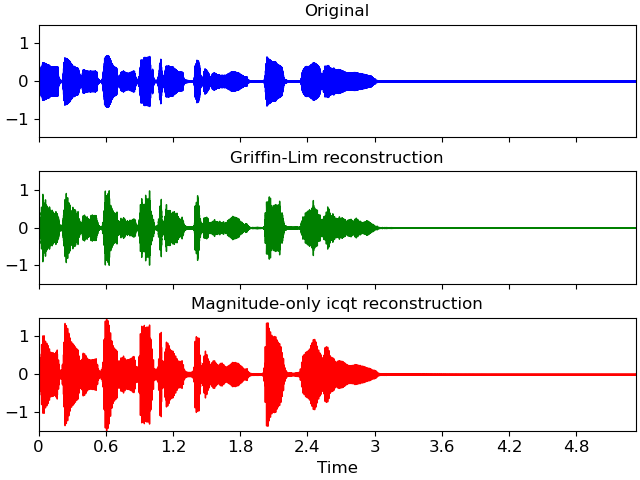
A basis CQT inverse example
>>> y, sr = librosa.load(librosa.ex('trumpet', hq=True), sr=None) >>> # Get the CQT magnitude, 7 octaves at 36 bins per octave >>> C = np.abs(librosa.cqt(y=y, sr=sr, bins_per_octave=36, n_bins=7*36)) >>> # Invert using Griffin-Lim >>> y_inv = librosa.griffinlim_cqt(C, sr=sr, bins_per_octave=36) >>> # And invert without estimating phase >>> y_icqt = librosa.icqt(C, sr=sr, bins_per_octave=36)
Wave-plot the results
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=3, sharex=True, sharey=True) >>> librosa.display.waveshow(y, sr=sr, color='b', ax=ax[0]) >>> ax[0].set(title='Original', xlabel=None) >>> ax[0].label_outer() >>> librosa.display.waveshow(y_inv, sr=sr, color='g', ax=ax[1]) >>> ax[1].set(title='Griffin-Lim reconstruction', xlabel=None) >>> ax[1].label_outer() >>> librosa.display.waveshow(y_icqt, sr=sr, color='r', ax=ax[2]) >>> ax[2].set(title='Magnitude-only icqt reconstruction')