Caution
You're reading an old version of this documentation. If you want up-to-date information, please have a look at 0.10.2.
librosa.iirt
- librosa.iirt(y, *, sr=22050, win_length=2048, hop_length=None, center=True, tuning=0.0, pad_mode='constant', flayout='sos', res_type='soxr_hq', **kwargs)[source]
Time-frequency representation using IIR filters
This function will return a time-frequency representation using a multirate filter bank consisting of IIR filters. [1]
First,
yis resampled as needed according to the providedsample_rates.Then, a filterbank with with
nband-pass filters is designed.The resampled input signals are processed by the filterbank as a whole. (
scipy.signal.filtfiltresp. sosfiltfilt is used to make the phase linear.) The output of the filterbank is cut into frames. For each band, the short-time mean-square power (STMSP) is calculated by summingwin_lengthsubsequent filtered time samples.When called with the default set of parameters, it will generate the TF-representation (pitch filterbank):
85 filters with MIDI pitches [24, 108] as
center_freqs.each filter having a bandwidth of one semitone.
- Parameters:
- ynp.ndarray [shape=(…, n)]
audio time series. Multi-channel is supported.
- srnumber > 0 [scalar]
sampling rate of
y- win_lengthint > 0, <= n_fft
Window length.
- hop_lengthint > 0 [scalar]
Hop length, number samples between subsequent frames. If not supplied, defaults to
win_length // 4.- centerboolean
If
True, the signalyis padded so that frameD[..., :, t]is centered aty[t * hop_length].If
False, then D[…, :, t]` begins aty[t * hop_length]
- tuningfloat [scalar]
Tuning deviation from A440 in fractions of a bin.
- pad_modestring
If
center=True, the padding mode to use at the edges of the signal. By default, this function uses zero padding.- flayoutstring
If sos (default), a series of second-order filters is used for filtering with
scipy.signal.sosfiltfilt. Minimizes numerical precision errors for high-order filters, but is slower.If ba, the standard difference equation is used for filtering with
scipy.signal.filtfilt. Can be unstable for high-order filters.
- res_typestring
The resampling mode. See
librosa.resamplefor details.- **kwargsadditional keyword arguments
Additional arguments for
librosa.filters.semitone_filterbank(e.g., could be used to provide another set ofcenter_freqsandsample_rates).
- Returns:
- bands_powernp.ndarray [shape=(…, n, t), dtype=dtype]
Short-time mean-square power for the input signal.
- Raises:
- ParameterError
If
flayoutis not None, ba, or sos.
See also
Examples
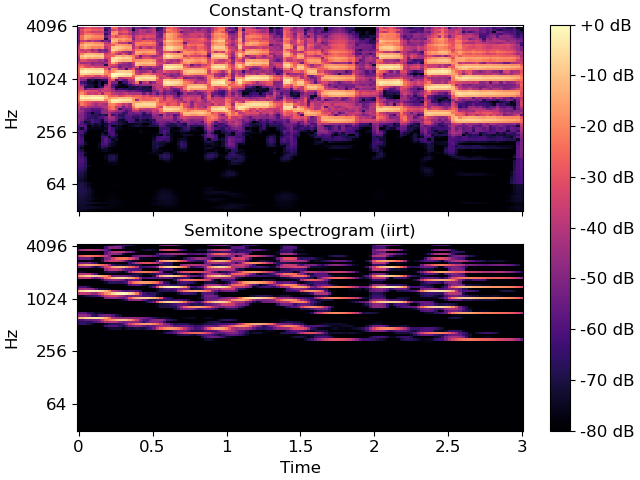
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> y, sr = librosa.load(librosa.ex('trumpet'), duration=3) >>> D = np.abs(librosa.iirt(y)) >>> C = np.abs(librosa.cqt(y=y, sr=sr)) >>> fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=2, sharex=True, sharey=True) >>> img = librosa.display.specshow(librosa.amplitude_to_db(C, ref=np.max), ... y_axis='cqt_hz', x_axis='time', ax=ax[0]) >>> ax[0].set(title='Constant-Q transform') >>> ax[0].label_outer() >>> img = librosa.display.specshow(librosa.amplitude_to_db(D, ref=np.max), ... y_axis='cqt_hz', x_axis='time', ax=ax[1]) >>> ax[1].set_title('Semitone spectrogram (iirt)') >>> fig.colorbar(img, ax=ax, format="%+2.0f dB")