Caution
You're reading an old version of this documentation. If you want up-to-date information, please have a look at 0.10.2.
librosa.feature.inverse.mel_to_stft
- librosa.feature.inverse.mel_to_stft(M, sr=22050, n_fft=2048, power=2.0, **kwargs)[source]
Approximate STFT magnitude from a Mel power spectrogram.
- Parameters:
- Mnp.ndarray [shape=(n_mels, n), non-negative]
The spectrogram as produced by feature.melspectrogram
- srnumber > 0 [scalar]
sampling rate of the underlying signal
- n_fftint > 0 [scalar]
number of FFT components in the resulting STFT
- powerfloat > 0 [scalar]
Exponent for the magnitude melspectrogram
- kwargsadditional keyword arguments
Mel filter bank parameters. See
librosa.filters.melfor details
- Returns:
- Snp.ndarray [shape=(n_fft, t), non-negative]
An approximate linear magnitude spectrogram
Examples
>>> y, sr = librosa.load(librosa.ex('trumpet')) >>> S = np.abs(librosa.stft(y)) >>> mel_spec = librosa.feature.melspectrogram(S=S, sr=sr) >>> S_inv = librosa.feature.inverse.mel_to_stft(mel_spec, sr=sr)
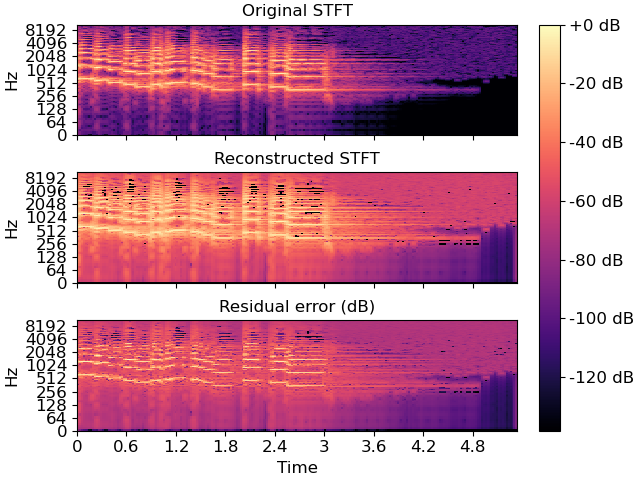
Compare the results visually
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=3, sharex=True, sharey=True) >>> img = librosa.display.specshow(librosa.amplitude_to_db(S, ref=np.max, top_db=None), ... y_axis='log', x_axis='time', ax=ax[0]) >>> ax[0].set(title='Original STFT') >>> ax[0].label_outer() >>> librosa.display.specshow(librosa.amplitude_to_db(S_inv, ref=np.max, top_db=None), ... y_axis='log', x_axis='time', ax=ax[1]) >>> ax[1].set(title='Reconstructed STFT') >>> ax[1].label_outer() >>> librosa.display.specshow(librosa.amplitude_to_db(np.abs(S_inv - S), ... ref=S.max(), top_db=None), ... vmax=0, y_axis='log', x_axis='time', cmap='magma', ax=ax[2]) >>> ax[2].set(title='Residual error (dB)') >>> fig.colorbar(img, ax=ax, format="%+2.f dB")