Caution
You're reading the documentation for a development version. For the latest released version, please have a look at 0.11.0.
librosa.decompose.hpss
- librosa.decompose.hpss(S, *, kernel_size=31, power=2.0, mask=False, margin=1.0)[source]
Median-filtering harmonic percussive source separation (HPSS).
If
margin = 1.0, decomposes an input spectrogramS = H + PwhereHcontains the harmonic components, andPcontains the percussive components.If
margin > 1.0, decomposes an input spectrogramS = H + P + RwhereRcontains residual components not included inHorP.This implementation is based upon the algorithm described by [1] and [2].
- Parameters:
- Snp.ndarray [shape=(…, d, n)]
input spectrogram. May be real (magnitude) or complex. Multi-channel is supported.
- kernel_sizeint or tuple (kernel_harmonic, kernel_percussive)
kernel size(s) for the median filters.
If scalar, the same size is used for both harmonic and percussive.
If tuple, the first value specifies the width of the harmonic filter, and the second value specifies the width of the percussive filter.
- powerfloat > 0 [scalar]
Exponent for the Wiener filter when constructing soft mask matrices.
- maskbool
Return the masking matrices instead of components.
Masking matrices contain non-negative real values that can be used to measure the assignment of energy from
Sinto harmonic or percussive components.Components can be recovered by multiplying
S * mask_HorS * mask_P.- marginfloat or tuple (margin_harmonic, margin_percussive)
margin size(s) for the masks (as described in [2])
If scalar, the same size is used for both harmonic and percussive.
If tuple, the first value specifies the margin of the harmonic mask, and the second value specifies the margin of the percussive mask.
- Returns:
- harmonicnp.ndarray [shape=(…, d, n)]
harmonic component (or mask)
- percussivenp.ndarray [shape=(…, d, n)]
percussive component (or mask)
See also
Notes
This function caches at level 30.
Examples
Separate into harmonic and percussive
>>> y, sr = librosa.load(librosa.ex('choice'), duration=5) >>> D = librosa.stft(y) >>> H, P = librosa.decompose.hpss(D)
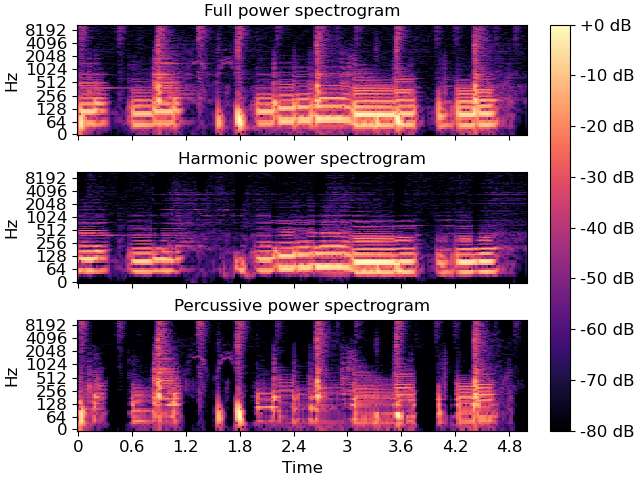
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=3, sharex=True, sharey=True) >>> img = librosa.display.specshow(librosa.amplitude_to_db(np.abs(D), ... ref=np.max), ... y_axis='log', x_axis='time', ax=ax[0]) >>> ax[0].set(title='Full power spectrogram') >>> ax[0].label_outer() >>> librosa.display.specshow(librosa.amplitude_to_db(np.abs(H), ... ref=np.max(np.abs(D))), ... y_axis='log', x_axis='time', ax=ax[1]) >>> ax[1].set(title='Harmonic power spectrogram') >>> ax[1].label_outer() >>> librosa.display.specshow(librosa.amplitude_to_db(np.abs(P), ... ref=np.max(np.abs(D))), ... y_axis='log', x_axis='time', ax=ax[2]) >>> ax[2].set(title='Percussive power spectrogram') >>> fig.colorbar(img, ax=ax, format='%+2.0f dB')
Or with a narrower horizontal filter
>>> H, P = librosa.decompose.hpss(D, kernel_size=(13, 31))
Just get harmonic/percussive masks, not the spectra
>>> mask_H, mask_P = librosa.decompose.hpss(D, mask=True) >>> mask_H array([[1.853e-03, 1.701e-04, ..., 9.922e-01, 1.000e+00], [2.316e-03, 2.127e-04, ..., 9.989e-01, 1.000e+00], ..., [8.195e-05, 6.939e-05, ..., 3.105e-04, 4.231e-04], [3.159e-05, 4.156e-05, ..., 6.216e-04, 6.188e-04]], dtype=float32) >>> mask_P array([[9.981e-01, 9.998e-01, ..., 7.759e-03, 3.201e-05], [9.977e-01, 9.998e-01, ..., 1.122e-03, 4.451e-06], ..., [9.999e-01, 9.999e-01, ..., 9.997e-01, 9.996e-01], [1.000e+00, 1.000e+00, ..., 9.994e-01, 9.994e-01]], dtype=float32)
Separate into harmonic/percussive/residual components by using a margin > 1.0
>>> H, P = librosa.decompose.hpss(D, margin=3.0) >>> R = D - (H+P) >>> y_harm = librosa.istft(H) >>> y_perc = librosa.istft(P) >>> y_resi = librosa.istft(R)
Get a more isolated percussive component by widening its margin
>>> H, P = librosa.decompose.hpss(D, margin=(1.0,5.0))