Caution
You're reading an old version of this documentation. If you want up-to-date information, please have a look at 0.9.1.
librosa.beat.plp¶
- librosa.beat.plp(y=None, sr=22050, onset_envelope=None, hop_length=512, win_length=384, tempo_min=30, tempo_max=300, prior=None)[source]¶
Predominant local pulse (PLP) estimation. [1]
The PLP method analyzes the onset strength envelope in the frequency domain to find a locally stable tempo for each frame. These local periodicities are used to synthesize local half-waves, which are combined such that peaks coincide with rhythmically salient frames (e.g. onset events on a musical time grid). The local maxima of the pulse curve can be taken as estimated beat positions.
This method may be preferred over the dynamic programming method of
beat_trackwhen either the tempo is expected to vary significantly over time. Additionally, sinceplpdoes not require the entire signal to make predictions, it may be preferable when beat-tracking long recordings in a streaming setting.- 1
Grosche, P., & Muller, M. (2011). “Extracting predominant local pulse information from music recordings.” IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 19(6), 1688-1701.
- Parameters
- ynp.ndarray [shape=(n,)] or None
audio time series
- srnumber > 0 [scalar]
sampling rate of y
- onset_envelopenp.ndarray [shape=(n,)] or None
(optional) pre-computed onset strength envelope
- hop_lengthint > 0 [scalar]
number of audio samples between successive onset_envelope values
- win_lengthint > 0 [scalar]
number of frames to use for tempogram analysis. By default, 384 frames (at sr=22050 and hop_length=512) corresponds to about 8.9 seconds.
- tempo_min, tempo_maxnumbers > 0 [scalar], optional
Minimum and maximum permissible tempo values. tempo_max must be at least tempo_min.
Set either (or both) to None to disable this constraint.
- priorscipy.stats.rv_continuous [optional]
A prior distribution over tempo (in beats per minute). By default, a uniform prior over [tempo_min, tempo_max] is used.
- Returns
- pulsenp.ndarray, shape=[(n,)]
The estimated pulse curve. Maxima correspond to rhythmically salient points of time.
Examples
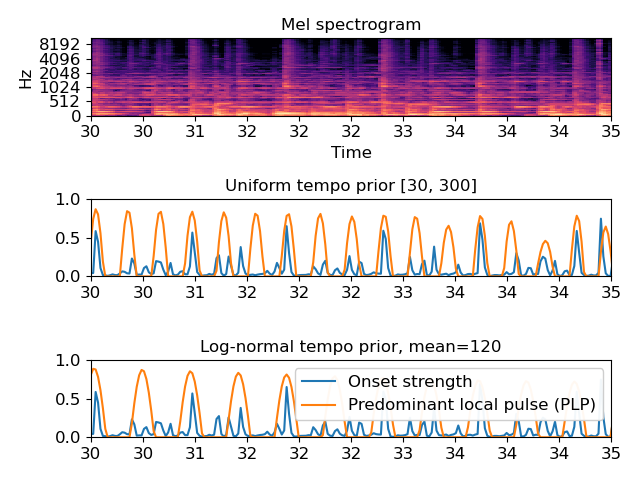
Visualize the PLP compared to an onset strength envelope. Both are normalized here to make comparison easier.
>>> y, sr = librosa.load(librosa.util.example_audio_file()) >>> onset_env = librosa.onset.onset_strength(y=y, sr=sr) >>> pulse = librosa.beat.plp(onset_envelope=onset_env, sr=sr) >>> # Or compute pulse with an alternate prior, like log-normal >>> import scipy.stats >>> prior = scipy.stats.lognorm(loc=np.log(120), scale=120, s=1) >>> pulse_lognorm = librosa.beat.plp(onset_envelope=onset_env, sr=sr, ... prior=prior) >>> melspec = librosa.feature.melspectrogram(y=y, sr=sr) >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> ax = plt.subplot(3,1,1) >>> librosa.display.specshow(librosa.power_to_db(melspec, ... ref=np.max), ... x_axis='time', y_axis='mel') >>> plt.title('Mel spectrogram') >>> plt.subplot(3,1,2, sharex=ax) >>> plt.plot(librosa.times_like(onset_env), ... librosa.util.normalize(onset_env), ... label='Onset strength') >>> plt.plot(librosa.times_like(pulse), ... librosa.util.normalize(pulse), ... label='Predominant local pulse (PLP)') >>> plt.title('Uniform tempo prior [30, 300]') >>> plt.subplot(3,1,3, sharex=ax) >>> plt.plot(librosa.times_like(onset_env), ... librosa.util.normalize(onset_env), ... label='Onset strength') >>> plt.plot(librosa.times_like(pulse_lognorm), ... librosa.util.normalize(pulse_lognorm), ... label='Predominant local pulse (PLP)') >>> plt.title('Log-normal tempo prior, mean=120') >>> plt.legend() >>> plt.xlim([30, 35]) >>> plt.tight_layout() >>> plt.show()
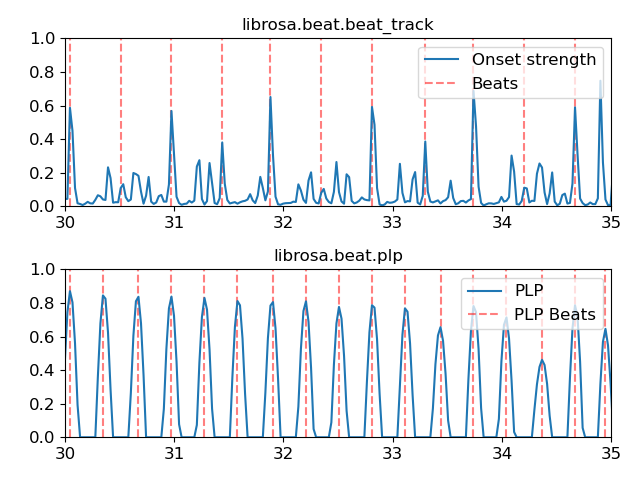
PLP local maxima can be used as estimates of beat positions.
>>> tempo, beats = librosa.beat.beat_track(onset_envelope=onset_env) >>> beats_plp = np.flatnonzero(librosa.util.localmax(pulse)) >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> ax = plt.subplot(2,1,1) >>> times = librosa.times_like(onset_env, sr=sr) >>> plt.plot(times, librosa.util.normalize(onset_env), ... label='Onset strength') >>> plt.vlines(times[beats], 0, 1, alpha=0.5, color='r', ... linestyle='--', label='Beats') >>> plt.legend(frameon=True, framealpha=0.75) >>> plt.title('librosa.beat.beat_track') >>> # Limit the plot to a 15-second window >>> plt.subplot(2,1,2, sharex=ax) >>> times = librosa.times_like(pulse, sr=sr) >>> plt.plot(times, librosa.util.normalize(pulse), ... label='PLP') >>> plt.vlines(times[beats_plp], 0, 1, alpha=0.5, color='r', ... linestyle='--', label='PLP Beats') >>> plt.legend(frameon=True, framealpha=0.75) >>> plt.title('librosa.beat.plp') >>> plt.xlim(30, 35) >>> ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(librosa.display.TimeFormatter()) >>> plt.tight_layout() >>> plt.show()