Caution
You're reading an old version of this documentation. If you want up-to-date information, please have a look at 0.9.1.
librosa.segment.subsegment¶
- librosa.segment.subsegment(data, frames, n_segments=4, axis=- 1)[source]¶
Sub-divide a segmentation by feature clustering.
Given a set of frame boundaries (frames), and a data matrix (data), each successive interval defined by frames is partitioned into n_segments by constrained agglomerative clustering.
Note
If an interval spans fewer than n_segments frames, then each frame becomes a sub-segment.
- Parameters
- datanp.ndarray
Data matrix to use in clustering
- framesnp.ndarray [shape=(n_boundaries,)], dtype=int, non-negative]
Array of beat or segment boundaries, as provided by
librosa.beat.beat_track,librosa.onset.onset_detect, oragglomerative.- n_segmentsint > 0
Maximum number of frames to sub-divide each interval.
- axisint
Axis along which to apply the segmentation. By default, the last index (-1) is taken.
- Returns
- boundariesnp.ndarray [shape=(n_subboundaries,)]
List of sub-divided segment boundaries
See also
agglomerativeTemporal segmentation
librosa.onset.onset_detectOnset detection
librosa.beat.beat_trackBeat tracking
Notes
This function caches at level 30.
Examples
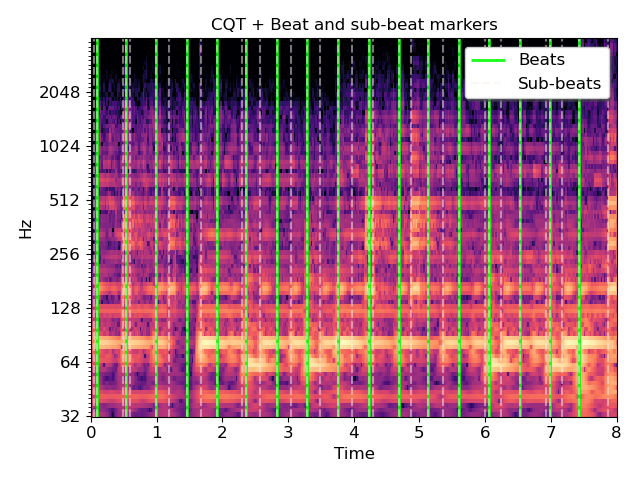
Load audio, detect beat frames, and subdivide in twos by CQT
>>> y, sr = librosa.load(librosa.util.example_audio_file(), duration=8) >>> tempo, beats = librosa.beat.beat_track(y=y, sr=sr, hop_length=512) >>> beat_times = librosa.frames_to_time(beats, sr=sr, hop_length=512) >>> cqt = np.abs(librosa.cqt(y, sr=sr, hop_length=512)) >>> subseg = librosa.segment.subsegment(cqt, beats, n_segments=2) >>> subseg_t = librosa.frames_to_time(subseg, sr=sr, hop_length=512) >>> subseg array([ 0, 2, 4, 21, 23, 26, 43, 55, 63, 72, 83, 97, 102, 111, 122, 137, 142, 153, 162, 180, 182, 185, 202, 210, 221, 231, 241, 256, 261, 271, 281, 296, 301, 310, 320, 339, 341, 344, 361, 368, 382, 389, 401, 416, 420, 430, 436, 451, 456, 465, 476, 489, 496, 503, 515, 527, 535, 544, 553, 558, 571, 578, 590, 607, 609, 638])
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> plt.figure() >>> librosa.display.specshow(librosa.amplitude_to_db(cqt, ... ref=np.max), ... y_axis='cqt_hz', x_axis='time') >>> lims = plt.gca().get_ylim() >>> plt.vlines(beat_times, lims[0], lims[1], color='lime', alpha=0.9, ... linewidth=2, label='Beats') >>> plt.vlines(subseg_t, lims[0], lims[1], color='linen', linestyle='--', ... linewidth=1.5, alpha=0.5, label='Sub-beats') >>> plt.legend(frameon=True, shadow=True) >>> plt.title('CQT + Beat and sub-beat markers') >>> plt.tight_layout() >>> plt.show()