Caution
You're reading an old version of this documentation. If you want up-to-date information, please have a look at 0.9.1.
librosa.core.salience¶
- librosa.core.salience(S, freqs, h_range, weights=None, aggregate=None, filter_peaks=True, fill_value=nan, kind='linear', axis=0)[source]¶
Harmonic salience function.
- Parameters
- Snp.ndarray [shape=(d, n)]
input time frequency magnitude representation (e.g. STFT or CQT magnitudes). Must be real-valued and non-negative.
- freqsnp.ndarray, shape=(S.shape[axis])
The frequency values corresponding to S’s elements along the chosen axis.
- h_rangelist-like, non-negative
Harmonics to include in salience computation. The first harmonic (1) corresponds to S itself. Values less than one (e.g., 1/2) correspond to sub-harmonics.
- weightslist-like
The weight to apply to each harmonic in the summation. (default: uniform weights). Must be the same length as harmonics.
- aggregatefunction
aggregation function (default: np.average) If aggregate=np.average, then a weighted average is computed per-harmonic according to the specified weights. For all other aggregation functions, all harmonics are treated equally.
- filter_peaksbool
If true, returns harmonic summation only on frequencies of peak magnitude. Otherwise returns harmonic summation over the full spectrum. Defaults to True.
- fill_valuefloat
The value to fill non-peaks in the output representation. (default: np.nan) Only used if filter_peaks == True.
- kindstr
Interpolation type for harmonic estimation. See
scipy.interpolate.interp1d.- axisint
The axis along which to compute harmonics
- Returns
- S_salnp.ndarray, shape=(len(h_range), [x.shape])
S_sal will have the same shape as S, and measure the overal harmonic energy at each frequency.
See also
Examples
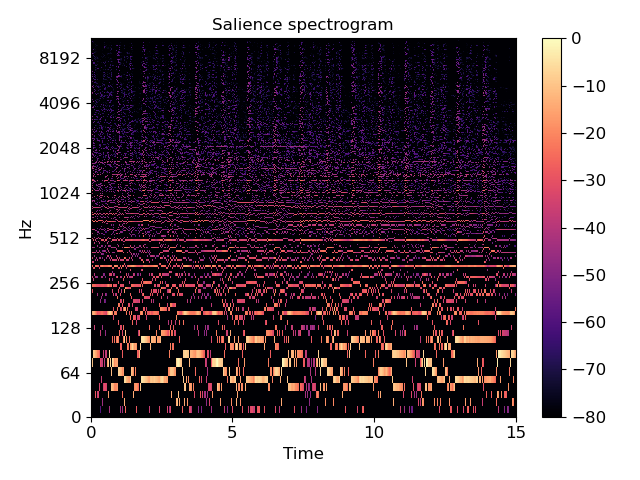
>>> y, sr = librosa.load(librosa.util.example_audio_file(), ... duration=15, offset=30) >>> S = np.abs(librosa.stft(y)) >>> freqs = librosa.core.fft_frequencies(sr) >>> harms = [1, 2, 3, 4] >>> weights = [1.0, 0.5, 0.33, 0.25] >>> S_sal = librosa.salience(S, freqs, harms, weights, fill_value=0) >>> print(S_sal.shape) (1025, 646) >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> plt.figure() >>> librosa.display.specshow(librosa.amplitude_to_db(S_sal, ... ref=np.max), ... sr=sr, y_axis='log', x_axis='time') >>> plt.colorbar() >>> plt.title('Salience spectrogram') >>> plt.tight_layout() >>> plt.show()