Caution
You're reading an old version of this documentation. If you want up-to-date information, please have a look at 0.9.1.
librosa.feature.chroma_cqt¶
- librosa.feature.chroma_cqt(y=None, sr=22050, C=None, hop_length=512, fmin=None, norm=inf, threshold=0.0, tuning=None, n_chroma=12, n_octaves=7, window=None, bins_per_octave=None, cqt_mode='full')[source]¶
Constant-Q chromagram
- Parameters
- ynp.ndarray [shape=(n,)]
audio time series
- srnumber > 0
sampling rate of y
- Cnp.ndarray [shape=(d, t)] [Optional]
a pre-computed constant-Q spectrogram
- hop_lengthint > 0
number of samples between successive chroma frames
- fminfloat > 0
minimum frequency to analyze in the CQT. Default: ‘C1’ ~= 32.7 Hz
- normint > 0, +-np.inf, or None
Column-wise normalization of the chromagram.
- thresholdfloat
Pre-normalization energy threshold. Values below the threshold are discarded, resulting in a sparse chromagram.
- tuningfloat
Deviation (in fractions of a CQT bin) from A440 tuning
- n_chromaint > 0
Number of chroma bins to produce
- n_octavesint > 0
Number of octaves to analyze above fmin
- windowNone or np.ndarray
Optional window parameter to filters.cq_to_chroma
- bins_per_octaveint > 0
Number of bins per octave in the CQT. Default: matches n_chroma
- cqt_mode[‘full’, ‘hybrid’]
Constant-Q transform mode
- Returns
- chromagramnp.ndarray [shape=(n_chroma, t)]
The output chromagram
Examples
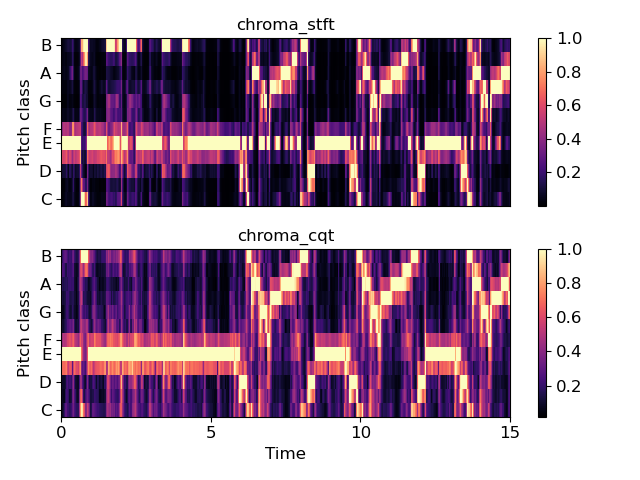
Compare a long-window STFT chromagram to the CQT chromagram
>>> y, sr = librosa.load(librosa.util.example_audio_file(), ... offset=10, duration=15) >>> chroma_stft = librosa.feature.chroma_stft(y=y, sr=sr, ... n_chroma=12, n_fft=4096) >>> chroma_cq = librosa.feature.chroma_cqt(y=y, sr=sr)
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> plt.figure() >>> plt.subplot(2,1,1) >>> librosa.display.specshow(chroma_stft, y_axis='chroma') >>> plt.title('chroma_stft') >>> plt.colorbar() >>> plt.subplot(2,1,2) >>> librosa.display.specshow(chroma_cq, y_axis='chroma', x_axis='time') >>> plt.title('chroma_cqt') >>> plt.colorbar() >>> plt.tight_layout() >>> plt.show()