Caution
You're reading an old version of this documentation. If you want up-to-date information, please have a look at 0.9.1.
librosa.feature.mfcc¶
- librosa.feature.mfcc(y=None, sr=22050, S=None, n_mfcc=20, dct_type=2, norm='ortho', lifter=0, **kwargs)[source]¶
Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCCs)
- Parameters
- ynp.ndarray [shape=(n,)] or None
audio time series
- srnumber > 0 [scalar]
sampling rate of y
- Snp.ndarray [shape=(d, t)] or None
log-power Mel spectrogram
- n_mfcc: int > 0 [scalar]
number of MFCCs to return
- dct_type{1, 2, 3}
Discrete cosine transform (DCT) type. By default, DCT type-2 is used.
- normNone or ‘ortho’
If dct_type is 2 or 3, setting norm=’ortho’ uses an ortho-normal DCT basis.
Normalization is not supported for dct_type=1.
- lifternumber >= 0
If lifter>0, apply liftering (cepstral filtering) to the MFCCs:
M[n, :] <- M[n, :] * (1 + sin(pi * (n + 1) / lifter)) * lifter / 2
Setting lifter >= 2 * n_mfcc emphasizes the higher-order coefficients. As lifter increases, the coefficient weighting becomes approximately linear.
- kwargsadditional keyword arguments
Arguments to
melspectrogram, if operating on time series input
- Returns
- Mnp.ndarray [shape=(n_mfcc, t)]
MFCC sequence
See also
Examples
Generate mfccs from a time series
>>> y, sr = librosa.load(librosa.util.example_audio_file(), offset=30, duration=5) >>> librosa.feature.mfcc(y=y, sr=sr) array([[ -5.229e+02, -4.944e+02, ..., -5.229e+02, -5.229e+02], [ 7.105e-15, 3.787e+01, ..., -7.105e-15, -7.105e-15], ..., [ 1.066e-14, -7.500e+00, ..., 1.421e-14, 1.421e-14], [ 3.109e-14, -5.058e+00, ..., 2.931e-14, 2.931e-14]])
Using a different hop length and HTK-style Mel frequencies
>>> librosa.feature.mfcc(y=y, sr=sr, hop_length=1024, htk=True) array([[-1.628e+02, -8.903e+01, -1.409e+02, ..., -1.078e+02, -2.504e+02, -2.393e+02], [ 1.275e+02, 9.532e+01, 1.019e+02, ..., 1.152e+02, 2.224e+02, 1.750e+02], [ 1.139e+01, 6.155e+00, 1.266e+01, ..., 4.557e+01, 4.585e+01, 3.985e+01], ..., [ 3.462e+00, 4.032e+00, -5.694e-01, ..., -6.677e+00, -1.183e-01, 1.485e+00], [ 9.569e-01, 1.069e+00, -6.865e+00, ..., -9.598e+00, -1.611e+00, -6.716e+00], [ 8.457e+00, 3.582e+00, -1.156e-01, ..., -3.018e+00, -1.456e+01, -6.991e+00]], dtype=float32)
Use a pre-computed log-power Mel spectrogram
>>> S = librosa.feature.melspectrogram(y=y, sr=sr, n_mels=128, ... fmax=8000) >>> librosa.feature.mfcc(S=librosa.power_to_db(S)) array([[ -5.207e+02, -4.898e+02, ..., -5.207e+02, -5.207e+02], [ -2.576e-14, 4.054e+01, ..., -3.997e-14, -3.997e-14], ..., [ 7.105e-15, -3.534e+00, ..., 0.000e+00, 0.000e+00], [ 3.020e-14, -2.613e+00, ..., 3.553e-14, 3.553e-14]])
Get more components
>>> mfccs = librosa.feature.mfcc(y=y, sr=sr, n_mfcc=40)
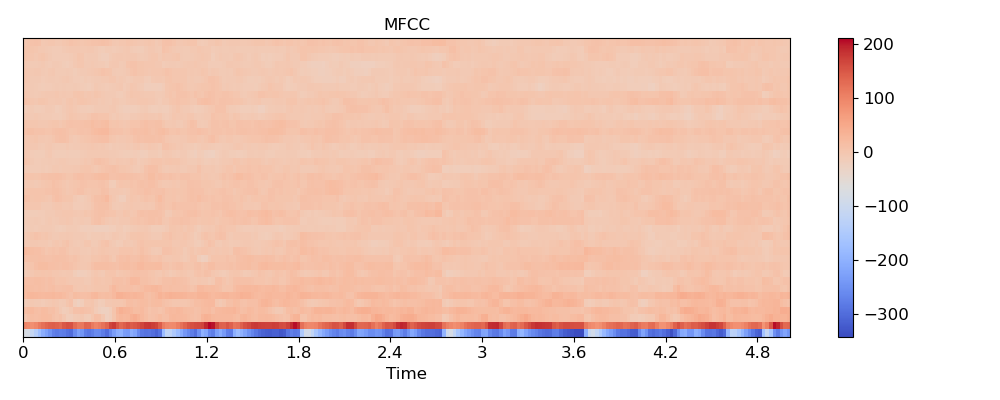
Visualize the MFCC series
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> plt.figure(figsize=(10, 4)) >>> librosa.display.specshow(mfccs, x_axis='time') >>> plt.colorbar() >>> plt.title('MFCC') >>> plt.tight_layout() >>> plt.show()
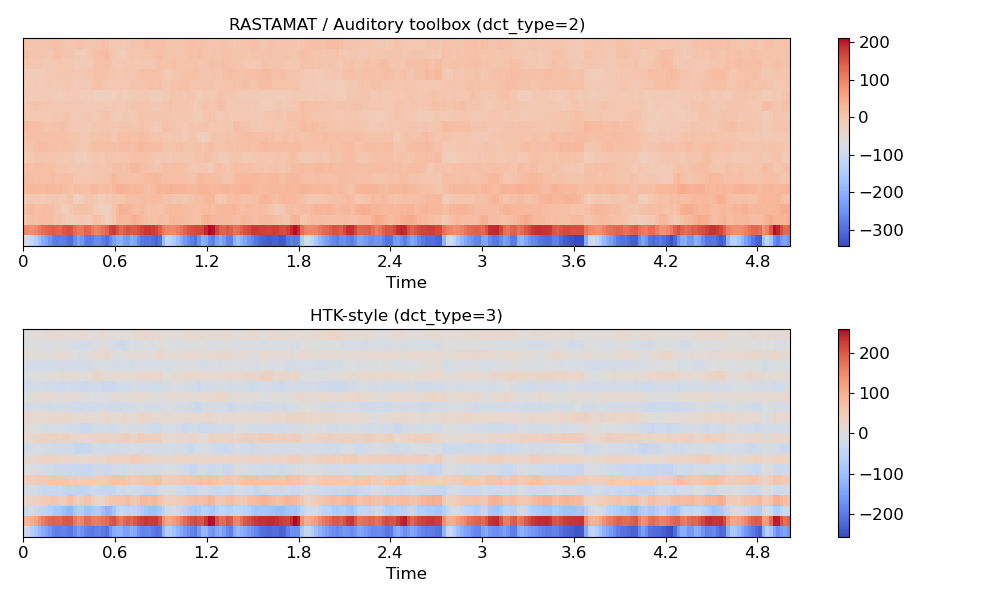
Compare different DCT bases
>>> m_slaney = librosa.feature.mfcc(y=y, sr=sr, dct_type=2) >>> m_htk = librosa.feature.mfcc(y=y, sr=sr, dct_type=3) >>> plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6)) >>> plt.subplot(2, 1, 1) >>> librosa.display.specshow(m_slaney, x_axis='time') >>> plt.title('RASTAMAT / Auditory toolbox (dct_type=2)') >>> plt.colorbar() >>> plt.subplot(2, 1, 2) >>> librosa.display.specshow(m_htk, x_axis='time') >>> plt.title('HTK-style (dct_type=3)') >>> plt.colorbar() >>> plt.tight_layout() >>> plt.show()