Caution
You're reading an old version of this documentation. If you want up-to-date information, please have a look at 0.9.1.
librosa.feature.rms¶
- librosa.feature.rms(y=None, S=None, frame_length=2048, hop_length=512, center=True, pad_mode='reflect')[source]¶
Compute root-mean-square (RMS) value for each frame, either from the audio samples y or from a spectrogram S.
Computing the RMS value from audio samples is faster as it doesn’t require a STFT calculation. However, using a spectrogram will give a more accurate representation of energy over time because its frames can be windowed, thus prefer using S if it’s already available.
- Parameters
- ynp.ndarray [shape=(n,)] or None
(optional) audio time series. Required if S is not input.
- Snp.ndarray [shape=(d, t)] or None
(optional) spectrogram magnitude. Required if y is not input.
- frame_lengthint > 0 [scalar]
length of analysis frame (in samples) for energy calculation
- hop_lengthint > 0 [scalar]
hop length for STFT. See
librosa.core.stftfor details.- centerbool
If True and operating on time-domain input (y), pad the signal by frame_length//2 on either side.
If operating on spectrogram input, this has no effect.
- pad_modestr
Padding mode for centered analysis. See np.pad for valid values.
- Returns
- rmsnp.ndarray [shape=(1, t)]
RMS value for each frame
Examples
>>> y, sr = librosa.load(librosa.util.example_audio_file()) >>> librosa.feature.rms(y=y) array([[ 0. , 0.056, ..., 0. , 0. ]], dtype=float32)
Or from spectrogram input
>>> S, phase = librosa.magphase(librosa.stft(y)) >>> rms = librosa.feature.rms(S=S)
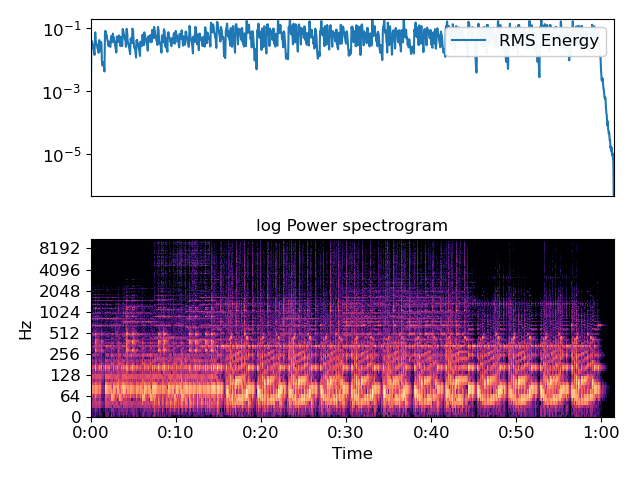
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> plt.figure() >>> plt.subplot(2, 1, 1) >>> plt.semilogy(rms.T, label='RMS Energy') >>> plt.xticks([]) >>> plt.xlim([0, rms.shape[-1]]) >>> plt.legend() >>> plt.subplot(2, 1, 2) >>> librosa.display.specshow(librosa.amplitude_to_db(S, ref=np.max), ... y_axis='log', x_axis='time') >>> plt.title('log Power spectrogram') >>> plt.tight_layout()
Use a STFT window of constant ones and no frame centering to get consistent results with the RMS computed from the audio samples y
>>> S = librosa.magphase(librosa.stft(y, window=np.ones, center=False))[0] >>> librosa.feature.rms(S=S) >>> plt.show()